10 Common Materials That Can Be 3D Printed

Did you know that 3D printing technology is not limited to just plastic? In fact, there are a wide variety of materials that can be used to create three-dimensional objects. From metals and ceramics to food and even human tissue, the possibilities are truly endless. In this article, we will explore 10 common materials that can be 3D printed, showcasing the versatility and innovation of this fascinating technology. So, whether you’re curious about the future of manufacturing or simply interested in the latest advancements, keep reading to discover the incredible array of materials that can be brought to life with a 3D printer.
Polylactic Acid (PLA)
Overview
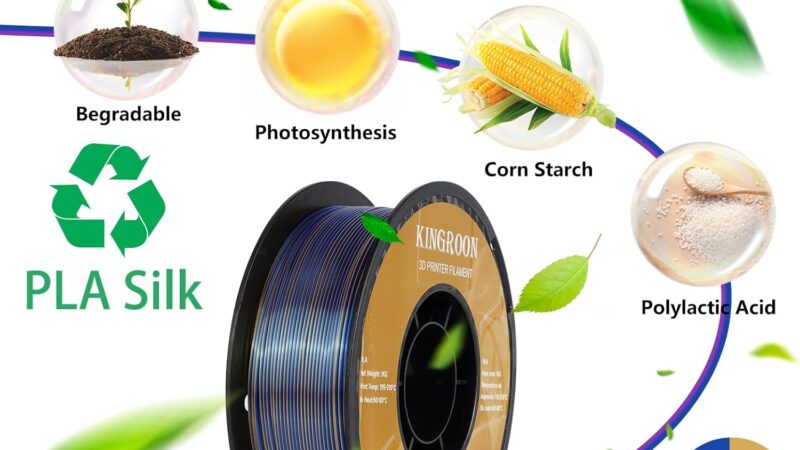
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is one of the most popular materials for 3D printing due to its ease of use, wide availability, and biodegradable nature. PLA is derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, making it a more sustainable option compared to traditional plastics. It is a thermoplastic polymer that can be easily melted and molded into various shapes using a 3D printer.
Properties
PLA exhibits excellent printability, which means it can produce highly detailed and intricate prints with minimal issues like warping or shrinkage. It has a low melting point, typically around 180-220 degrees Celsius, making it compatible with most consumer-grade 3D printers. PLA is also available in a wide range of vibrant colors, allowing for creative and visually appealing prints.
While PLA is generally not as strong or heat-resistant as other materials, it still possesses decent mechanical properties. It has good tensile strength, rigidity, and impact resistance, making it suitable for a wide variety of applications. PLA also has low toxicity and is considered food-safe, which further expands its potential use-cases.
Applications
PLA’s versatility and ease of use make it suitable for numerous applications. It is commonly used for prototyping, hobby projects, and educational purposes due to its affordability and accessibility. PLA is also extensively used in the production of figurines, toys, and decorations, thanks to its vibrant colors and fine print quality.
Additionally, PLA’s biodegradable nature makes it a popular choice for eco-conscious individuals and businesses. It can be used for manufacturing disposable items like cutlery, packaging materials, and even medical implants. PLA’s growing popularity and availability have led to its use in more specialized fields like biomedical and architectural applications.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Overview
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is another widely used material in 3D printing. It is a thermoplastic polymer that offers excellent durability and impact resistance. ABS is derived from petrochemical sources and is known for its toughness and high heat tolerance, making it suitable for more demanding applications.
Properties
ABS exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to PLA, making it a preferred choice for functional parts and prototypes. It has a higher melting point of around 210-250 degrees Celsius, which makes it more suitable for printing objects that may be exposed to higher temperatures. ABS is known for its high impact resistance and can withstand more stress and strain compared to PLA.
However, ABS can be slightly more challenging to print with due to its tendency to warp or shrink during cooling. To mitigate this issue, ABS often requires a heated build platform or an enclosed printer to maintain consistent temperature and prevent warping. Additionally, ABS emits potentially harmful fumes during printing, so it is recommended to use it in well-ventilated areas or with air filtration systems.
Applications
ABS is commonly used in industrial and engineering applications where stronger and more durable parts are required. It is frequently used in automotive manufacturing for components like car interiors, dashboard trims, and protective covers due to its ability to withstand high temperatures and impact. ABS is also favored for the production of functional prototypes, tools, and jigs, thanks to its toughness and durability.
Furthermore, ABS’s range of available colors and excellent post-processing capabilities, such as sanding and painting, make it suitable for creating aesthetically pleasing products. It is often utilized in the production of consumer goods, household items, and electronics casings. While ABS is not biodegradable like PLA, it is recyclable, which adds to its sustainability credentials.

This image is property of pixabay.com.
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG)
Overview
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG) is a popular choice for 3D printing enthusiasts seeking a balance between durability, printability, and clarity. PETG is derived from PET, which is commonly used in the production of plastic bottles. It combines the properties of both PLA and ABS, making it a versatile material for various applications.
Properties
PETG offers excellent layer adhesion during printing, resulting in strong and sturdy printed parts. It has a lower melting point than ABS, typically around 220-250 degrees Celsius, which makes it compatible with a broader range of 3D printers. PETG is known for its transparency and clarity, making it suitable for objects that require a see-through or glass-like appearance.
In terms of mechanical properties, PETG exhibits good impact resistance and flexibility, similar to ABS. It also boasts better chemical resistance compared to PLA and ABS, making it more resistant to solvents and certain liquids. Additionally, PETG is less prone to warping or shrinking during printing, reducing the chances of print failures.
Applications
PETG’s unique combination of properties makes it a popular choice for functional parts and mechanical prototypes. It finds applications in industries such as robotics, aerospace, and automotive, where durability and impact resistance are crucial. PETG’s transparency and resistance to chemicals and moisture also make it suitable for creating containers, bottles, and food-safe packaging.
Furthermore, PETG’s ease of use and printability, similar to PLA, make it a go-to material for beginner 3D printing enthusiasts. It can be used to create a wide range of objects, including toys, figurines, and various household items. PETG’s biocompatibility also allows for its utilization in the medical field, such as medical device prototypes and prosthetics.
The versatility of PETG expands further with its compatibility for post-processing techniques like sanding, painting, and dyeing. This enables the production of customized and visually appealing objects, making it a popular choice in the artistic and creative realm of 3D printing.
Polypropylene (PP)
Overview
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer that offers unique properties, making it suitable for specific applications in 3D printing. It is commonly used in industry sectors where chemical resistance, low density, and flexibility are critical factors.
Properties
PP possesses several distinct properties that set it apart from other materials. It has a low density, making objects printed with polypropylene lightweight and easy to handle. PP is also known for its excellent chemical resistance, withstanding exposure to acids, solvents, and bases. This property makes it ideal for parts that may come into contact with potentially corrosive substances.
Moreover, PP exhibits good fatigue resistance and flexibility, allowing for the creation of functional parts that endure repeated stress and strain. It also has a high melting point, typically ranging from 160 to 190 degrees Celsius, depending on the specific grade of PP used.
Applications
PP’s unique combination of properties makes it valuable in several industries and applications. It is commonly used in the automotive sector for manufacturing components like bumpers, interior trims, and battery casings due to its lightweight nature and impact resistance. PP is also utilized in the production of chemical-resistant containers, packaging, and plumbing systems.
In 3D printing, PP is ideal for creating functional prototypes and objects that require resistance to chemicals, temperature variations, and flexibility. Its low density and durability enable the production of lightweight but strong parts in sectors like robotics, instruments, and mechanical engineering. PP’s resistance to moisture and UV radiation also render it suitable for outdoor applications, such as garden tools and structures.
Polypropylene filament may require certain adjustments to optimize print settings and prevent warping. Some printers may benefit from using a heated chamber or modifying the printing environment to maintain a constant temperature throughout the print job.

This image is property of pixabay.com.
Nylon
Overview
Nylon, a versatile thermoplastic material, has gained popularity in the field of 3D printing due to its excellent mechanical properties and durability. It is well-suited for applications requiring toughness, resistance to impact and wear, and the ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Properties
Nylon filament possesses high strength, making it one of the toughest materials available for 3D printing. It is highly resistant to impact and can absorb considerable energy before breaking, making it ideal for printing functional parts subjected to stress and strain. Nylon also has excellent wear resistance, allowing for prolonged use without significant degradation.
This material is notable for its ability to be flexible and elastic, with varying degrees of rigidity depending on the specific nylon grade chosen. Additionally, nylon has good chemical resistance, making it suitable for applications that may involve exposure to oils, solvents, and other corrosive substances.
Applications
Nylon’s exceptional properties make it a popular choice in numerous industrial and functional applications. It is widely used in the production of gears, bearings, and bushings due to its excellent wear resistance and self-lubricating properties. Nylon is also favored for manufacturing functional prototypes, jigs, and fixtures in the engineering and automotive sectors.
Additionally, nylon’s versatility extends to the sports and recreation industry, where it is utilized for producing equipment like bicycle frames, protective gear, and sports gear components. The material’s resistance to UV radiation allows it to withstand outdoor conditions, making it suitable for applications such as brackets, clips, and hinges in architectural and construction projects.
However, nylon’s higher printing temperature requirements and unique characteristics, such as moisture absorption, may require specific considerations during the printing process. It is recommended to dry nylon filaments before use and control the printing environment to achieve optimal results.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Overview
Polycarbonate (PC) is a strong, transparent thermoplastic material that has gained popularity in 3D printing due to its combination of toughness and optical clarity. It is known for its excellent impact strength, heat resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures.
Properties
PC exhibits exceptional mechanical properties, making it suitable for functional prototypes and parts that require high strength and rigidity. It has a high impact resistance, allowing it to endure considerable force without shattering or breaking. Polycarbonate also possesses excellent heat resistance, maintaining its structural integrity at high temperatures up to approximately 110-130 degrees Celsius.
Furthermore, PC has superb optical clarity, similar to glass, making it a preferred material for applications that require transparency or see-through characteristics. It is also known for its high dimensional stability, meaning printed parts made of polycarbonate will maintain their shape and size over time.
Applications
Polycarbonate’s unique combination of toughness, heat resistance, and optical clarity opens a wide range of applications across multiple industries. It is extensively used in the automotive sector for producing parts like headlight housings, brackets, and interior components due to its durability and heat resistance.
PC’s outstanding impact strength and transparency make it an excellent choice for safety equipment like helmet visors and protective shields. It is also utilized in the electrical and electronics industry for manufacturing housings, connectors, and other intricate components.
Additionally, polycarbonate’s resistance to harsh weather conditions and UV radiation makes it ideal for outdoor applications such as signage, enclosures, and protective covers. Its optical clarity, coupled with its dimensional stability, enables the creation of prototypes, lenses, and light-guiding elements for industries like optics and lighting.
Polycarbonate’s high melting temperature necessitates a 3D printer capable of achieving and maintaining the required elevated printing temperatures. Additionally, printing with PC may require a heated bed or an enclosed chamber to prevent warping and maintain optimal printing conditions.

This image is property of pixabay.com.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Overview
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a versatile thermoplastic known for its strength, rigidity, and resistance to chemicals and moisture. It is commonly used in 3D printing applications that require durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Properties
HDPE exhibits excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and impact resistance. It is a lightweight material with a low density, making it suitable for applications where weight reduction is desired. HDPE is also notable for its resistance to chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents, as well as its resistance to moisture, making it suitable for outdoor or water-exposed applications.
Furthermore, HDPE is known for its electrical insulating properties, allowing it to be used in applications that require insulation or dielectric properties. It also possesses excellent UV resistance, ensuring its durability in outdoor environments with prolonged exposure to sunlight.
Applications
HDPE’s combination of strength, chemical resistance, and environmental durability makes it a suitable choice for various applications across different industries. It is commonly used in the production of pipes, tubes, and fittings due to its resistance to corrosion and build-up. HDPE is also favored for packaging materials, tanks, and containers that store chemicals, detergents, or other substances.
Additionally, HDPE is utilized in the creation of outdoor furniture, playground equipment, and recreational items due to its resistance to UV radiation and moisture. Its lightweight nature and durability make it ideal for building materials like lightweight walls and panels.
In the realm of 3D printing, HDPE is often utilized for prototyping, functional parts, and mechanical components that require excellent strength and resistance to chemical exposure. While HDPE can be more challenging to print compared to other materials, its unique properties make it valuable for specific applications.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Overview
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) is a flexible and elastomeric material widely used in 3D printing applications where flexibility, durability, and impact resistance are critical. TPU belongs to a family of polyurethane materials known for their rubber-like characteristics.
Properties
TPU is known for its exceptional flexibility, high elongation at break, and resistance to tearing. It can stretch significantly and return to its original shape without permanent deformation. This property makes TPU ideal for printing objects that require elasticity, gaskets, and parts subjected to repetitive bending or stretching.
Furthermore, TPU exhibits excellent resistance to oils, greases, and solvents, as well as abrasion resistance, ensuring the longevity of printed parts. It also has good UV resistance, allowing it to maintain its properties even when exposed to sunlight over extended periods.
Applications
TPU’s rubber-like properties and high flexibility make it suitable for a wide range of functional and specialized applications. It is commonly used in the production of footwear, such as shoe soles and insoles, due to its cushioning and shock absorption properties. TPU is also favored in the sports and fitness industry for creating flexible components in sports equipment, including mouthguards, wristbands, and protective gear.
In 3D printing, TPU is used for producing prototyping models, seals, soft-touch grips, and gaskets for various industries. Its ability to be printed in different durometers allows for the creation of custom parts with varying levels of hardness and flexibility.
TPU may require specific settings and equipment to achieve optimal results during the printing process. It is recommended to use a direct drive extruder or a Bowden setup depending on the printer’s design and characteristics that best suit TPU filament.

Wood Filament
Overview
Wood filament is a unique material that combines a base polymer with fine wood particles, resulting in prints that resemble wood objects both visually and tactilely. It enables the creation of objects with a natural and organic appearance without the challenges and limitations of traditional woodworking.
Properties
Wood filament offers a range of properties that make it distinct from conventional materials. It exhibits a textured surface, grain-like appearance, and a pleasant woody scent. These characteristics result in prints that closely resemble real wood, opening up opportunities for creative and decorative applications.
Wood filament also retains some of the mechanical properties associated with its base polymer, such as PLA or ABS, giving it strength and rigidity similar to those materials. This allows for functional applications that evoke a natural aesthetic, such as wooden-inspired tabletop accessories or decorative elements with intricate wood-like details.
Applications
Wood filament’s unique properties make it highly sought after in artistic and craft-based applications. It is commonly used for producing home decor items, sculptures, figurines, and models that possess the warmth and texture of wood. Wood filament allows for the creation of personalized wooden signs, jewelry, and ornaments with ease, providing a visually appealing, natural, and organic touch.
It is essential to note that wood filament may require a larger nozzle size to accommodate the wood particles and reduce the likelihood of clogging during the printing process. Experimenting with different printing settings and parameters can help achieve optimal results and enhance the desired wood-like finish.
Metal Filament
Overview
Metal filament, also known as metal-infused or metal-filled filament, allows for the creation of 3D printed objects with metallic properties without the need for specialized metal 3D printers or powder-based techniques. It blends a base polymer with a fine metal powder, enabling the production of prints that resemble metal objects.
Properties
Metal filament provides prints with several properties typically associated with metal, such as a metallic appearance, weight, and thermal conductivity. The metal powder mixed into the filament can be composed of various metals, including copper, bronze, iron, or stainless steel, resulting in different finishes and effects.
However, it is crucial to note that while metal filament imparts a metallic appearance, the printed object itself does not possess the same strength and properties as pure metal. The final prints are generally not as strong or malleable as their metal counterparts due to the limitations of the printing process.
Applications
Metal filament finds applications in various areas that benefit from the metallic appearance and finish. It is commonly used in the creation of jewelry, accessories, and sculptures that require the visual and tactile qualities of metal. The ability to 3D print metal-like objects provides designers and artisans with greater flexibility and customization options.
Furthermore, metal filament opens doors in industries such as cosplay and prop-making, allowing for the production of lightweight, cost-effective metallic components. It can also be utilized for architectural models, prototypes, and mock-ups that require a metallic aesthetic to showcase intricate details realistically.
Prints made with metal filament may require additional post-processing techniques to enhance the metallic appearance, such as sanding, polishing, or even electroplating. These techniques can provide a smoother surface finish and additional shine, further enhancing the resemblance to metal.
In conclusion, 3D printing offers a wide range of choices when it comes to materials. From PLA and ABS to PETG, nylon, and beyond, each material has its unique set of properties and applications. Whether you are a hobbyist, a designer, or an industrial professional, understanding the characteristics of these materials can help you select the most suitable option for your 3D printing needs. So, have fun exploring different materials and unleash your creativity with the limitless possibilities of 3D printing!