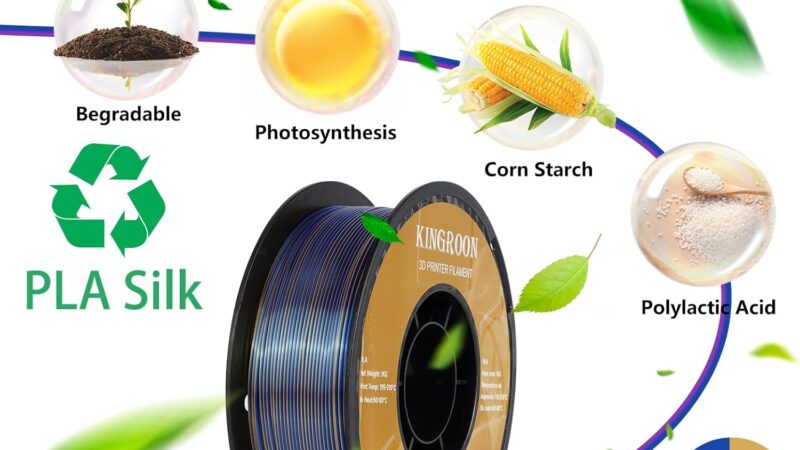
Understanding PLA Filament in 3D Printing

If you’re new to the world of 3D printing, you may have come across the term “PLA filament” and wondered what it is exactly. In this article, we’ll provide you with a clear and concise understanding of PLA filament in 3D printing. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, this article will help you grasp the basics of this versatile material and its significance in the world of additive manufacturing. So, let’s get started and unravel the wonders of PLA filament!
Understanding PLA Filament in 3D Printing
3D printing has revolutionized the way we create and prototype objects, and one of the most commonly used materials in this field is PLA filament. PLA, or Polylactic Acid, is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. It is widely favored by hobbyists, professionals, and manufacturers alike for its unique set of characteristics and ease of use.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Overview of PLA Filament
PLA filament is a type of 3D printing material that is popular for its user-friendly nature and versatility. With its low melting point, it is suitable for both Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Stereolithography (SLA) printers. PLA filament is formed by extruding the PLA polymer into thin and consistent strands, which can then be fed into a 3D printer for precise layer-by-layer deposition.
Advantages of PLA Filament
One of the key advantages of PLA filament is its environmental sustainability. Unlike other 3D printing materials like ABS, PLA is derived from renewable resources and is biodegradable, making it an eco-friendly choice. Additionally, PLA does not emit harmful fumes or odors during printing, making it safe for use in homes, offices, and classrooms.
Another advantage of PLA filament is its ease of use. It has excellent layer adhesion, which means that prints are less likely to warp or deform during the printing process. PLA also has a higher tolerance to heat, making it less prone to nozzle clogging compared to other materials like ABS. Furthermore, PLA filament is available in a wide range of vibrant colors, allowing for visually appealing prints.
Disadvantages of PLA Filament
While PLA filament offers numerous advantages, it also has some limitations to consider. One of the main disadvantages is its reduced temperature resistance compared to materials like ABS or PETG. PLA can deform or soften at temperatures above 60-65 degrees Celsius, making it unsuitable for applications where high heat exposure is expected.
Another drawback of PLA filament is its brittleness. PLA tends to be more brittle compared to other filaments, which means that printed objects may be more prone to cracking or breaking under stress. This limits its use in applications that require high impact resistance or flexibility.
Properties of PLA Filament
Understanding the properties of PLA filament is essential for achieving successful 3D prints. PLA has a relatively low glass transition temperature of around 60 degrees Celsius, which means that the material can transition from a solid to a rubbery state at this temperature. This property allows PLA to maintain its shape during printing but limits its use in high-temperature environments.
PLA also boasts good dimensional stability, which ensures that prints retain their shape and size over time. It has a low shrinkage rate compared to other materials, reducing the risk of warping or distortion during the cooling process. Additionally, PLA filament has excellent printability due to its low viscosity, providing smooth and consistent extrusions.
This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Choosing the Right PLA Filament
When selecting PLA filament, there are several factors to consider. First and foremost, it is essential to choose a reputable manufacturer to ensure consistent quality and reliable performance. Pay attention to any certifications or standards the filament may have, as these can indicate higher quality standards.
The diameter of the filament is another crucial aspect to consider. Common diameters for PLA filaments are 1.75mm and 2.85mm, so make sure your printer is compatible with the chosen diameter. Additionally, some PLA filaments are enhanced with additives or modifications to enhance specific properties such as strength, flexibility, or heat resistance. Consider your intended application and select the appropriate PLA filament accordingly.
Preparing PLA Filament for 3D Printing
Before you start 3D printing with PLA filament, it is essential to properly prepare and store the filament. PLA is prone to absorbing moisture from the surrounding environment, which can negatively impact print quality. It is recommended to store PLA filament in a sealed container with desiccant to prevent moisture absorption.
To ensure smooth extrusion and reduce the risk of nozzle clogging, it is crucial to check the condition of the filament before printing. Inspect the filament for any signs of dust, debris, or knots that may hinder the feeding process. Additionally, make sure the filament spool is properly mounted on the printer to allow for smooth unwinding.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Printing with PLA Filament
Once the PLA filament is prepared, it’s time to start the 3D printing process. Before you begin printing, it is crucial to calibrate the printer to ensure accurate layer deposition. Adjust the nozzle height, build plate levelness, and ensure the correct printing temperature is set for PLA filament.
When printing with PLA, it is generally recommended to use a heated build plate, although it is not mandatory. A heated build plate can help improve adhesion and minimize warping, especially when printing larger objects. However, if your printer does not have a heated build plate, applying painter’s tape or using a specialized build surface can also enhance bed adhesion.
Post-Processing PLA Prints
Once the printing is complete, it’s time for post-processing to achieve the desired finish. PLA prints typically do not require extensive post-processing, as PLA has a smooth surface finish and minimal visible layer lines. However, if desired, you can sand or polish the print to achieve a smoother appearance.
If you need to join multiple PLA parts, adhesive bonding or friction welding techniques can be used. PLA is also compatible with painting and dyeing, allowing for customization and aesthetic improvements. However, keep in mind that surface preparation, such as sanding and priming, may be required for optimal paint adhesion.
Common Troubleshooting Issues with PLA
While printing with PLA filament is generally straightforward, there are a few common troubleshooting issues that may arise. One of the most frequent issues is poor bed adhesion, resulting in prints detaching from the build plate or warping. To address this, ensure that the build plate is clean and properly leveled, and consider using a build plate adhesive like hairspray or glue stick.
Another common problem is stringing or oozing, where thin wisps of filament appear between printed components. To minimize this issue, adjust the retraction settings in your slicer software and experiment with different print speeds and temperatures. Additionally, ensure that the printer is properly calibrated to prevent excessive filament extrusion.
Future Developments in PLA Filament Technology
As 3D printing technology continues to advance, so does the development of PLA filament. Researchers are constantly working on improving the mechanical properties of PLA to enhance its strength, flexibility, and heat resistance. This ongoing research aims to expand the range of applications where PLA filament can be used, including in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and healthcare.
Another area of focus is the development of biocompatible and bioresorbable PLA filaments. These filaments have the potential to revolutionize the medical field by enabling the production of custom implants and tissue scaffolds. The biodegradable nature of PLA further contributes to reducing waste and environmental impact, making it a promising material for sustainable manufacturing in the future.
In conclusion, PLA filament is a versatile and eco-friendly material widely used in 3D printing. Its unique properties and ease of use make it suitable for a wide range of applications, from prototyping to manufacturing functional parts. By understanding the advantages, disadvantages, and proper handling techniques, you can maximize your 3D printing experience with PLA filament and unlock its full potential in your projects.