Innovative Materials for 3D Printing

Imagine a world where you can print objects in three dimensions, using materials that were previously unimaginable. Well, that world is becoming a reality as innovative materials for 3D printing are continually being developed. From biodegradable plastic to metal alloys, the possibilities are endless when it comes to creating intricate and complex structures with this revolutionary technology. In this article, we will explore the exciting range of materials that can be used in 3D printing, unlocking a world of endless possibilities right at your fingertips.
Innovative Materials for 3D Printing
Welcome to the world of 3D printing! In this article, we will explore a wide range of materials that can be used in 3D printing. From plastics to metals, ceramics to composites, bio-based materials to advanced synthetics, conductive materials to magnetic materials, and even optical materials – the possibilities are endless. So, let’s dive into the exciting world of 3D printing materials!
1. Plastics
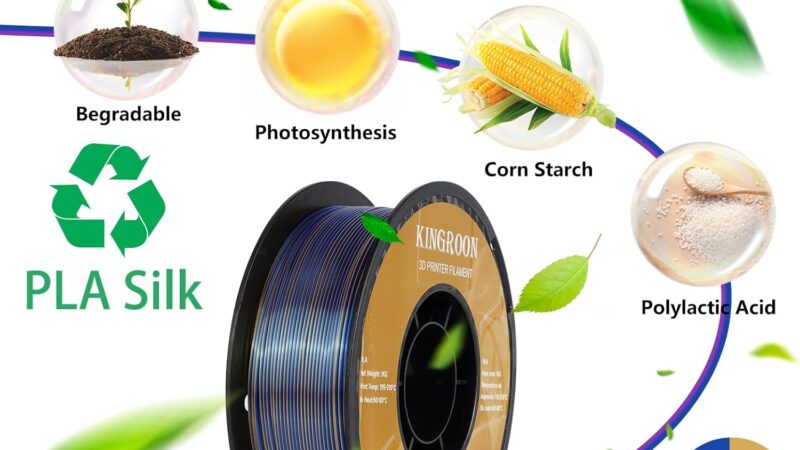
1.1 PLA
PLA, or Polylactic Acid, is one of the most commonly used materials in 3D printing. It is derived from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane, making it an eco-friendly choice. PLA is known for its ease of use, low shrinkage, and biodegradability. It is ideal for printing prototypes, models, and objects that do not require high temperature resistance.
1.2 ABS
ABS, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a popular thermoplastic used in 3D printing. It offers excellent strength, durability, and impact resistance. ABS is widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics due to its ability to withstand higher temperatures. However, it is important to note that ABS emits fumes during printing, so proper ventilation is necessary.
1.3 Nylon
Nylon is a versatile material that offers a combination of strength, flexibility, and durability. It is known for its high melting point, making it suitable for functional prototypes, mechanical parts, and even artistic designs. Nylon also has great resistance to wear, making it an ideal choice for applications that require friction resistance, such as gears and bearings.
1.4 PETG
PETG, or Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol, is a popular choice for 3D printing due to its ease of use and versatility. It offers a good balance of strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance. PETG is commonly used for prototyping, mechanical parts, and structural components. It is also known for its transparency and can be used to create clear or translucent objects.
2. Metals
2.1 Titanium
Titanium is a lightweight and strong metal that is widely used in various industries, including aerospace, medical, and automotive. 3D printing with titanium allows for complex geometries and customization. The resulting parts have excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Titanium 3D printing is often used in applications requiring high-performance and durability.
2.2 Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a widely used metal in industries ranging from architectural to medical. 3D printing with stainless steel provides the advantage of creating intricate designs and complex shapes. Stainless steel parts offer good strength, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance. The ability to customize and produce small batches of stainless steel components makes it a favorable choice in various applications.
2.3 Aluminum
Aluminum is a lightweight and highly versatile metal that finds its applications in aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods industries. 3D printing with aluminum allows for creating lightweight structures with good strength and thermal conductivity. Aluminum parts are known for their high durability, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity. This makes aluminum 3D printing an attractive option in a wide range of industries.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
3. Ceramics
3.1 Porcelain
Porcelain is a traditional ceramic material known for its elegance and beauty. 3D printing with porcelain allows for intricate and detailed designs. Porcelain parts have excellent heat resistance and are often used in artistic creations, jewelry, and even dental applications. The ability to create custom ceramic objects using 3D printing technology opens up new possibilities for artists and designers.
3.2 Zirconia
Zirconia is a ceramic material that offers high strength, biocompatibility, and resistance to wear and corrosion. 3D printing with zirconia enables the production of dental crowns, implants, and other medical devices. Zirconia parts also find applications in industries like aerospace and electronics, where high-performance ceramic components are required.
4. Composites
4.1 Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers
Carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRPs) combine the strength and lightweight properties of carbon fiber with the versatility of polymers. 3D printing with CFRPs allows for the creation of high-strength and lightweight structures. CFRPs are widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment manufacturing. They offer excellent stiffness, heat resistance, and durability.
4.2 Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers
Glass fiber reinforced polymers (GFRPs) combine the strength of glass fibers with the flexibility and versatility of polymers. 3D printing with GFRPs provides a cost-effective solution for producing high-performance parts. GFRPs find applications in various industries, including construction, automotive, and electrical. They offer good strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to chemicals and heat.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
5. Bio-based Materials
5.1 Biodegradable Polymers
Biodegradable polymers are derived from renewable resources and can break down naturally over time. 3D printing with biodegradable polymers offers an eco-friendly alternative for various applications. These materials are widely used in the medical field for creating biocompatible implants and surgical models. Biodegradable polymers also find applications in packaging, consumer goods, and other industries where sustainability is a priority.
5.2 Alginate
Alginate is a natural polymer derived from algae. It is commonly used in the food and medical industries. 3D printing with alginate enables the creation of complex shapes and structures. Alginate parts are often used in biomedical applications such as tissue engineering and drug delivery. Its biocompatibility and biodegradability make it a promising material for future medical advancements.
6. Rubber-like Materials
6.1 TPU
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is a flexible and rubber-like material widely used in 3D printing. TPU offers excellent elasticity, impact resistance, and durability. It is commonly used in industries such as footwear, consumer goods, and electronics. 3D printing with TPU allows for the creation of soft-touch parts, gaskets, seals, and other flexible components.
6.2 TPE
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) are a class of materials that combine the properties of rubber and plastic. TPEs offer good elasticity, resilience, and chemical resistance. 3D printing with TPE allows for the production of soft and flexible parts. TPE parts find applications in industries such as automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
7. Advanced Synthetics
7.1 PEEK
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical properties and chemical resistance. 3D printing with PEEK enables the production of parts with high strength, temperature resistance, and dimensional stability. PEEK finds applications in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries, where extreme conditions and high-performance requirements are common.
7.2 PEI
Polyetherimide (PEI) is a high-performance thermoplastic with exceptional electrical properties and dimensional stability. 3D printing with PEI offers the advantage of producing parts with high strength, heat resistance, and flame retardancy. PEI is widely used in industries such as electronics, automotive, and aerospace, where electrical insulation and structural integrity are crucial.
8. Conductive Materials
8.1 Carbon Nanotube Composites
Carbon nanotube composites are materials that incorporate carbon nanotubes into a polymer matrix. 3D printing with carbon nanotube composites allows for the production of conductive parts with unique electrical properties. These materials find applications in fields such as electronics, sensors, and energy storage devices. Carbon nanotube composites offer excellent conductivity, mechanical strength, and thermal stability.
8.2 Graphene
Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. 3D printing with graphene offers the advantage of creating conductive components with exceptional properties. Graphene parts find applications in electronics, aerospace, and energy storage. Graphene offers excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength, making it a fascinating material for future technological advancements.
9. Magnetic Materials
9.1 Magnetorheological Elastomers
Magnetorheological elastomers (MREs) are smart materials that change their mechanical properties in the presence of a magnetic field. 3D printing with MREs allows for the creation of parts with controllable stiffness, damping, and shape-shifting capabilities. MREs find applications in industries such as automotive, robotics, and prosthetics. Their ability to respond to magnetic fields enables the development of innovative devices and systems.
9.2 Magnets
Magnets are materials that produce a magnetic field and attract certain metals. 3D printing with magnets opens up new possibilities for creating complex magnetic structures and devices. Magnets find applications in various industries, including electronics, automotive, and renewable energy. Printed magnets offer customization, reduced waste, and efficiency in manufacturing processes.
10. Optical Materials
10.1 Clear Resins
Clear resins are transparent materials used in 3D printing to produce objects with optical clarity. 3D printing with clear resins enables the creation of prototypes, lenses, and other optical components. Clear resins are widely used in industries such as optics, medical, and consumer goods. They offer excellent light transmission, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy.
10.2 Transparent Plastics
Transparent plastics, such as acrylic and polycarbonate, offer a combination of strength and optical clarity. 3D printing with transparent plastics allows for the production of transparent objects, windows, and displays. Transparent plastics find applications in a wide range of industries, including automotive, architecture, and electronics. They offer good impact resistance, UV stability, and design flexibility.
10.3 Light-guiding Structures
Light-guiding structures are materials designed to control the propagation of light. 3D printing with light-guiding structures enables the creation of optical fibers, light pipes, and other light-guiding components. These materials find applications in industries such as telecommunications, lighting, and sensing. Light-guiding structures offer precise control over light transmission, reduced energy loss, and compact designs.
In conclusion, the world of 3D printing offers a vast array of innovative materials to bring your ideas to life. From plastics to metals, ceramics to composites, bio-based materials to advanced synthetics, conductive materials to magnetic materials, and even optical materials – there is a material for every application. So, unleash your creativity and explore the endless possibilities of 3D printing with these cutting-edge materials!