What is PLA filament?

You’re about to embark on a fascinating journey into the world of PLA filament, a term that may sound unfamiliar but holds immense potential for creative minds like yours. PLA filament, short for Polylactic Acid filament, is a type of 3D printing material that has been gaining popularity for its eco-friendly properties and versatility. From intricate prototypes to artistic sculptures, PLA filament offers an exciting avenue to bring your imaginative ideas to life. Let’s take a closer look at this revolutionary material and discover the endless possibilities it holds for your future projects.
This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
What is PLA Filament?
Overview of PLA filament
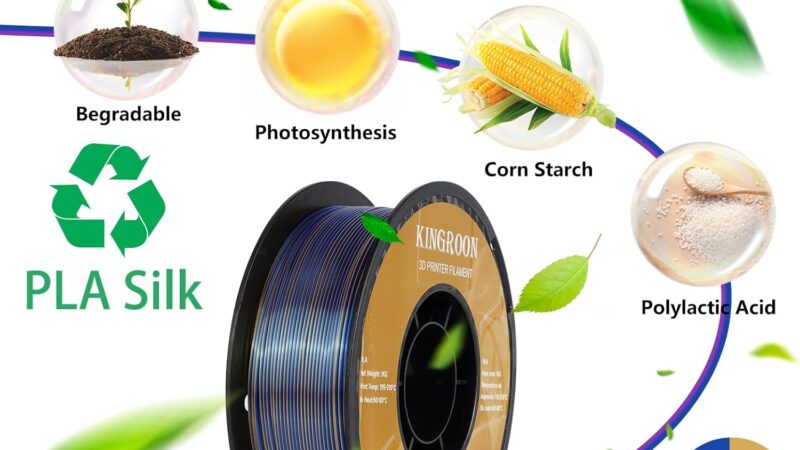
PLA filament, also known as Polylactic Acid filament, is a popular type of thermoplastic material used in 3D printing. It is derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane and is widely considered as an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional plastics. PLA filament is renowned for its ease of use, vibrant colors, and wide range of applications.
Composition of PLA filament
PLA filament is composed of polylactic acid, a biodegradable polyester derived from plant-based sources. The primary raw materials used in its production are corn starch and sugar cane, which undergo a complex process to convert them into PLA resin. This resin is then transformed into filament form, with the addition of certain additives to enhance its performance characteristics.
Properties of PLA filament
PLA filament exhibits several unique properties that make it a popular choice in the 3D printing community. Firstly, it has a relatively low melting point compared to other filaments, making it easier to work with. It also has a high tensile strength, meaning it can withstand significant pulling forces without breaking. Additionally, PLA filament is known for its rigidity, allowing it to maintain its shape after being printed.
Environmental impact of PLA filament
One of the key advantages of PLA filament is its positive environmental impact. As PLA is derived from renewable resources, such as corn starch and sugar cane, it is considered a sustainable and eco-friendly material. When PLA products, including filament, reach the end of their useful life, they can be composted in industrial composting facilities. This means they can break down into organic matter without contributing to landfill waste.
1. Overview of PLA Filament
Definition of PLA filament
PLA filament refers to the thermoplastic material used in 3D printing, which is composed of polylactic acid derived from renewable resources. It is a popular choice due to its ease of use, wide range of colors, and environmental benefits. PLA filament can be melted and extruded through a 3D printer nozzle to create intricate three-dimensional objects.
Types of PLA filament
There are various types of PLA filament available in the market, each offering unique characteristics and functionalities. Standard PLA filament is the most common type and is suitable for general-purpose printing. There are also variants such as ‘Silk PLA’ that provide a glossy finish, ‘Glow in the Dark PLA’ that emits light when exposed to darkness, and ‘Metal PLA’ that imitates the appearance of metallic materials. These different types of PLA filament allow for diverse and creative 3D printing projects.
This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
2. Composition of PLA Filament
Materials used in PLA filament production
The production of PLA filament involves the use of plant-based materials, primarily corn starch and sugar cane. These renewable resources are processed to extract the starch, which undergoes fermentation to produce lactic acid. Through a series of chemical reactions, lactic acid is then converted into polylactic acid (PLA) resin. This resin serves as the base material for manufacturing PLA filament.
Chemical structure of PLA filament
PLA filament consists of long chains of repeating units, known as monomers, linked together through ester bonds. The chemical structure and arrangement of these monomers determine the properties and behavior of PLA filament. The structure of PLA allows it to break down into its constituent components under the right conditions, making it biodegradable and environmentally friendly.

3. Properties of PLA Filament
Physical properties of PLA filament
PLA filament possesses distinct physical properties that contribute to its usability in 3D printing. It has a relatively low glass transition temperature, meaning it can change from a rigid state to a more flexible state when heated. This characteristic allows for easier layer adhesion during printing and reduces the chances of warping. PLA filament is also known for its vibrant colors, making it ideal for creating visually appealing and detailed models.
Mechanical properties of PLA filament
In terms of mechanical properties, PLA filament exhibits good tensile strength, which enables it to withstand pulling forces without breaking. It also has a high modulus of elasticity, meaning it maintains its shape and structure under stress. However, PLA is comparatively brittle compared to other filaments, which can result in its susceptibility to cracking or fracturing in certain applications. It is important to consider these mechanical properties when selecting PLA filament for specific projects.
Printability of PLA filament
One of the reasons for the widespread popularity of PLA filament is its excellent printability. It is compatible with a wide range of 3D printers and does not require a heated bed for successful printing, unlike some other filament types. PLA has good layer adhesion, resulting in smooth and detailed prints. However, it is worth noting that PLA has a tendency to string, meaning thin strands of material may be left behind during printing. This can be managed through printer settings and optimizing print parameters.
This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
4. Environmental Impact of PLA Filament
Biodegradability of PLA filament
One of the most significant environmental advantages of PLA filament is its biodegradability. PLA is a bioplastic that can be broken down by naturally occurring microorganisms, making it compostable. Under the right conditions, such as in industrial composting facilities, PLA filament can decompose within a few months, reducing its impact on the environment. It should be noted that home composting may take longer due to variations in temperature and microbial activity.
Renewability of PLA filament
Another aspect that contributes to the environmental impact of PLA filament is its renewability. PLA is derived from renewable resources, such as corn starch or sugar cane, which are continually replenished through agricultural processes. This contrasts with traditional plastics that rely on fossil fuels, a non-renewable resource. By using PLA filament, you are supporting a sustainable and resource-efficient approach to 3D printing.
Composting and recycling of PLA filament
When PLA filament reaches the end of its useful life, it can be composted in industrial composting facilities along with other organic waste. This means that PLA products, including 3D prints, have the potential to contribute to creating nutrient-rich soil instead of being discarded in landfills. It is important to note that PLA filament should not be recycled with other plastics, as its different chemical composition can contaminate recycling streams. Check with local recycling facilities for specific instructions on proper disposal and recycling of PLA filament.
In conclusion, PLA filament offers a range of benefits in terms of ease of use, versatility, and environmental sustainability. Its composition, properties, and environmental impact make it a compelling choice for 3D printing enthusiasts. By choosing PLA filament, you not only have access to a user-friendly material that produces high-quality prints but also contribute to reducing the environmental footprint associated with traditional plastics.